When your car won’t start with a jump start, there could be a lot of culprits behind that. A dead battery is the most common reason your car won’t start by jump-starting. It could be damaged for various reasons; the dome light was left on overnight, and water inside a component evaporated, resulting in poor conductivity.
Or, you have some corroded or loose battery connections that avert the charging system from topping off your battery when the car is functioning, a loose wire or the battery is just old. Make sure to follow all the safety and handling instructions on the battery before you try and fix the problem yourself. In this guide, we’ll be taking a look at why your car won’t start with a jump.
Besides all the most common reasons, we’ll also look at diagnosis and troubleshooting steps, as well as how to fix this issue for good. Moreover, we’ll discuss more tips and tricks, such as how to properly jump-start a car, and what to check first if your car won’t start. Also, there are some other handy guides here for maintaining your car’s battery.
- What Is A Jump-Start?
- How To Jump-Start A Car?
- What To Do & Check First?
- Why Your Car Won’t Start With A Jump?
- Troubleshooting Non-Start Issues
- Non-Battery Problems
- Battery Care & Maintenance
- DIY Repairs & Fixes
- Other Automotive No-Start Scenarios
- Tips On Choosing A Good Mechanic
- Final Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Jump Start Car
Jump-starting your vehicle means you’re getting a temporary boost for a discharged battery. Depending on why your battery shuts down, a jump start can possibly fix the issue and get your car moving.
By connecting your vehicle’s battery to another vehicle’s battery using jumper cables (once you’ve learned how to put on jumper cables), the other vehicle’s battery can transmit the electrical charge to your car’s battery powering your vehicle.
Once power is transferred via the cables to your vehicle, the alternator will turn on, and as you run the engine, your alternator continues to recharge your battery. If you run the engine long enough, either by letting it sit idle or by driving, you might recharge your battery and prevent any issues from building up.
This can be all you need to do to fix the issue with a low battery resulting from an accidental drain. If, for example, you accidentally left your radio or lights on overnight and drained your battery, jump-starting your car could get your vehicle moving again.
Should your car battery has a physical problem, as in it’s damaged in some way, then jump starting may not necessarily repair the battery. If it’s damaged, you don’t want to even jump-start, as that can result in a battery explosion.
How To Jump Start A Car
If your battery is dead, here’s what you need to do to properly and safely jump-start a car…
Step #1: Safely Position Your Vehicles
The first step in the jump-starting process is positioning the cars. Park both vehicles in close proximity to each other, either nose-to-nose or side-by-side, in a secure and non-traffic-intensive location. Make sure your vehicles are set up in such a way that the jumper cables can easily reach both batteries without being overly stretched.
Remember, safety is paramount. If your car breaks down on a busy road or highway, don’t attempt to move it on your own. Call for professional roadside assistance or a tow truck service.
Step #2: Identifying the Batteries in Both Vehicles
Next, locate the batteries in each car. Generally, batteries are found in the engine compartment, but some vehicles have them in less conventional spots such as the trunk or beneath a seat. If you can’t find the batteries, refer to each vehicle’s user manual for guidance.
If there are plastic covers on the batteries, carefully remove them and set them aside. Avoid any forceful tugging, which could damage the battery or your vehicle’s electrical system.
Step #3: Connecting the Cables to the Good Battery
Now, you’ll need to connect your jumper cables. Start with the positive (+) terminal of the working car’s battery, represented by the red clamp on your jumper cables. Make sure to hold the corresponding black clamp in your other hand and avoid any contact between the clamps on opposite ends of the cables, as this could cause a short circuit.
Subsequently, connect the black clamp to the negative (-) terminal on the working car’s battery. At this point, the cables are “live,” meaning they’re conducting electricity, so be extra careful not to touch any exposed metal parts of the clamps.
Step #4: Linking the Cables to the Non-Starting Vehicle
Next, connect the other red clamp to the positive (+) terminal on the dead car’s battery. Ensure that the black clamp in your other hand doesn’t come into contact with your skin or the car’s battery.
Then, attach the remaining black clamp to a ground point on the non-starting car, which could be the engine block or any exposed metal away from the battery. Do not connect it to the negative (-) terminal on the non-starting car.
Step #5: Starting the Vehicles
Start the working car and let it idle for a few minutes to charge the dead battery. After a few minutes, attempt to start the non-starting car. If it starts, let it run for a while to recharge its battery.
Step #6: Detaching the Jumper Cables
Once the jump-started car has been running for a while, it’s time to disconnect the cables. This should be done in the reverse order of how they were attached: start by removing the black clamp from the ground point on the jump-started car, then the red clamp from its battery.
Afterward, remove the red clamp from the working car’s battery and then the remaining black clamp. With all four clamps disconnected, the cables are no longer live and can be safely stored away.
Step #7: Final Checks and Steps
Before you proceed with your journey, try turning off the jump-started car and then starting it again. This ensures the battery has been charged sufficiently. If the car doesn’t start, it’s likely that the battery is beyond salvage and needs replacement. At this point, call for professional help or arrange for a replacement battery.
While jump-starting a car may seem straightforward, it’s essential to follow the correct steps and prioritize safety to prevent accidents and damage to your vehicle’s electrical system. Regular battery maintenance can help prevent the need for a jump-start, so keep an eye on your vehicle’s battery health and consult with a professional if you encounter persistent starting problems.
What Should You Check First If Your Car Won’t Start With Jump
Before we look at the reasons why your car won’t start with a jump, here are some things that you could do and check first…
1. Evaluating the Jumper Cable Connection
Firstly, ensure that your jumper cables are correctly connected. A common error can occur in the connection sequence, leading to a failure in jump-starting the vehicle. Ensure that the red clamps are attached to the positive terminals (+) and the black clamps to the negative terminals (-) on both batteries.
Always remember to connect the cables in this order: dead battery positive, live battery positive, live battery negative, and finally a grounded metal part on the dead car away from the battery.
2. Inspecting Jumper Cables
Cables in poor condition could hinder the transmission of power between vehicles. Before using jumper cables, it’s a good idea to inspect them for any signs of physical damage, such as fraying, loose clamps, or any signs of overheating, such as a warm rubber coating. Old or damaged jumper cables might not carry enough current to start the engine.
3. Assessing the Battery Terminals
Corroded battery terminals can impede the flow of electricity. Examine the terminals on your battery for any signs of rust or other deposits. If you spot corrosion, disconnect the battery, and use a wire brush to clean the posts. Rinse with a baking soda and water solution to neutralize any remaining acid, then dry thoroughly before reconnecting the battery.
4. Checking for Vehicle Power
Try switching the key forward without starting the engine. If the dashboard lights turn on, or if you can operate the radio, it suggests your car is receiving power but is unable to start. This could indicate an issue with the starting system rather than the battery.
5. Observing for Other Problems
A multitude of factors unrelated to the battery could be preventing your vehicle from starting. For instance, a dry gas tank, a blocked fuel filter, a faulty ignition switch, or a damaged starter could all lead to starting issues.
Take note of any other symptoms that might point to these problems. For example, a clicking noise could indicate a bad starter, while the smell of gasoline could suggest a flooded engine.
6. Consulting a Professional
If you’ve tried all of these steps and your car still refuses to start, it might be time to seek professional help. A certified mechanic can diagnose complex issues, such as problems with the car’s electronic systems or engine components, which could be beyond the scope of a layperson.
7. Regular Maintenance is Key
Prevention is always better than cure. Regular maintenance, including keeping your battery clean, ensuring the terminals are secure and corrosion-free, and getting your charging system checked regularly can prevent a multitude of starting issues.
Similarly, making sure to run your vehicle regularly can also help keep the battery in good shape. Neglecting this can lead to a dead battery, which might not jump-start.
Why Won’t My Car Start
There are many reasons why your car fails to start by jump-starting. Below are some of the reasons. However, some are more common than others.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #1: Dead Battery
A malfunctioning battery is the most common root cause of your car not being able to jump-start. The battery is the center of your car and delivers power to every part of your car to ensure it operates seamlessly.
Car batteries don’t last forever. Depending on the driving conditions and climate, expect to replace your car battery approximately every three years. A defective cell or an internal short circuit will prevent the battery from jump-starting. In that case, the ideal fix is a new battery.
If you have doubts about the condition of your battery, have it tested. With hand-held testers nowadays, the job only takes a few minutes. Many repair shops and auto part stores offer free testing. Not only will they examine your battery’s condition, but they will also test the starting and charging systems all at once.
Causes of a Dead Battery
A dead battery is the most frequent reason a car won’t start, even after attempting a jump-start. There are several reasons why a car battery might die:
- Excessive Short Trips: Your car battery recharges when you drive. However, frequent short trips prevent the battery from fully charging, which can gradually deplete it.
- Parasitic Drain: This happens when your car’s electrical devices continue to consume battery power after the ignition is off. Although some drain is normal (for alarm systems or car clock), excessive drain can result in a dead battery.
- Age: Batteries don’t last forever. Typically, they last about three years, but this can vary based on the usage and the climate. A battery nearing its end of life will have trouble holding a charge.
- Temperature Extremes: Batteries don’t perform well in extremely cold or hot temperatures. Extreme cold can slow down the chemical reaction inside a battery, reducing its power output. In contrast, high temperatures can cause the battery to overheat, leading to quicker degradation.
Symptoms of a Dead Battery
Other than the obvious symptom of your car not starting, there are several signs that might indicate a dead or dying battery:
- Dimming Headlights: If the headlights dim when you start your car or while it’s running, this could be a sign that the battery is not providing enough power.
- Slow Engine Crank: If the engine cranks slowly or not at all when you turn the ignition, it could be a battery issue.
- Check Engine Light: In some vehicles, the check engine light may turn on when the battery is weak.
- Corrosion on the Battery Terminals: Visible corrosion on the battery terminals can lead to poor electrical connections and a weak battery.
Troubleshooting a Dead Battery
To confirm that a dead battery is the issue, here are some steps to follow:
- Visual Inspection: Check the battery for signs of swelling, leaks, or corrosion on the terminals. These signs could indicate a bad battery.
- Battery Test: Many auto parts stores will test your battery for free. The test will determine if the battery can hold a charge.
- Check the Alternator: If the battery is good, the alternator might be the problem. If the alternator isn’t working correctly, it won’t charge the battery, and the battery will deplete quickly.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Dead Battery
While replacing the battery is often the best solution, here are some DIY fixes you can try:
- Cleaning the Battery Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can prevent the battery from charging. Cleaning the terminals might help.
- Battery Reconditioning: Some batteries can be reconditioned by fully draining and then recharging them. However, this is not recommended for all batteries. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines before attempting this.
Costs of Battery Replacement
If you need to replace your car battery, the cost can vary. On average, expect to pay between $100 and $200 for a new car battery. This includes the cost of the battery itself and the labor for installation. However, the exact price will depend on your vehicle’s make and model.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #2: A Faulty Alternator
A car battery can hardly meet all the needs of a vehicle’s electrical system. The alternator functions to restore electrical power to the battery lost when starting your vehicle. An alternator also powers electrical current to the vehicle’s electrical fixtures when the engine is running.
A faulty alternator will result in a completely discharged or undercharged battery with lower capacity and starting power. If your battery is constantly undercharged due to a weak or faulty alternator, it will more likely become excessively discharged, causing sulfation.
Some signs that you have a faulty alternator include:
- Your car’s gauges start to act strange.
- You notice the smell of burning rubber or hot wire that happens when the alternator is overheating.
- You notice a growling sound immediately before the alternator goes off.
- Your headlights or dashboard lights go dim or flicker.
Causes of a Faulty Alternator
The alternator plays a crucial role in keeping your car battery charged and powering the vehicle’s electrical systems. Several factors can cause an alternator to fail:
- Age and Wear: Like any other car part, alternators wear out over time. Mechanical parts can fail, or the alternator can become clogged with dirt and oil, reducing its effectiveness.
- Overloading: If you run many high-power accessories at once, you might overload the alternator, leading to failure. This is particularly the case with high-wattage sound systems or additional lighting.
- Poor Battery Condition: A faulty or dying battery can put extra strain on the alternator, causing it to work harder to keep the battery charged, leading to premature failure.
- Belt Issues: If the alternator belt is too tight, loose, or worn out, it can affect the alternator’s operation, potentially causing it to fail.
Symptoms of a Faulty Alternator
While a car not starting could be a sign of a faulty alternator, there are other symptoms to look for:
- Flickering or Dimming Lights: If the lights dim or flicker, this could be a sign that the alternator is not generating enough power.
- Warning Light: Many cars have a warning light on the dashboard labeled “ALT” or “GEN,” indicating a problem with the alternator.
- Strange Smells: An overheating alternator can cause a burning smell similar to hot rubber or wires.
- Unusual Sounds: If you hear a growling or whining noise, this could be a sign that the alternator bearings are failing.
Troubleshooting a Faulty Alternator
Here’s how you can confirm if the alternator is the problem:
- Use a Multimeter: You can use a multimeter to check the alternator’s output. With the engine running, the reading should be around 13.8 to 14.2 volts.
- Check the Serpentine Belt: Ensure the belt that drives the alternator isn’t slipping or broken.
- Take it to a Professional: If you’re unsure, take your vehicle to a mechanic. They can test the alternator and other components to confirm the issue.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Faulty Alternator
Fixing an alternator might be more complex than replacing a battery. Here are some steps you can take:
- Tighten or Replace the Belt: If the belt is loose, you might be able to tighten it. If it’s damaged, it’ll need to be replaced.
- Clean the Alternator: If the alternator is dirty or oily, cleaning it might improve its performance.
However, if these steps don’t help, you’ll likely need to replace the alternator.
Costs of Alternator Replacement
Replacing an alternator can be costly. On average, expect to pay between $500 and $1,000. The cost varies based on the make and model of your car and the labor costs in your area. Keep in mind, a faulty alternator can damage other parts of your vehicle, leading to additional costs down the line.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #3: Clogged Fuel Filter
Regardless of the engine type, all cars have fuel filters that clean the fuel before going to the engine. This step makes filters susceptible to debris build-up, resulting in a clogged fuel filter. And as a result, gasoline won’t be able to reach the engine leading to engine failure.
Make sure to replace your fuel filter accordingly to ensure your fuel filter remains clean and functional. Although the vehicle’s manufacturer manual offers precise details, most manufacturers recommend changing the fuel filter every 50,000 miles or five years. However, most mechanics see this estimate as too extreme and recommend replacing or cleaning it out every 10,000 miles.
Some signs of a clogged fuel filter include:
- Frequent idling or sputtering. Your vehicle’s engine will often start without any problem but will shut down when you try to stop. This implies that sufficient fuel goes through the filter while driving but deteriorates when the vehicle is idle.
- Trouble with accelerating. If upon trying to accelerate but your vehicle’s speed doesn’t necessarily change means that you probably have to change your fuel filter.
- Engine misfires or low performance.
- Strong odors from the vehicle’s exhaust.
Causes of a Clogged Fuel Filter
The fuel filter’s job is to keep debris out of the engine. However, this makes the filter susceptible to becoming clogged. Here’s what can cause this:
- Old Fuel Filter: Over time, fuel filters collect debris from the gasoline. If not replaced periodically, they can become clogged.
- Dirty Fuel: Low-quality or contaminated fuel can have more debris, which can lead to a clogged filter faster.
- Infrequent Maintenance: If the fuel filter isn’t replaced at the recommended intervals, it can easily become clogged.
Symptoms of a Clogged Fuel Filter
A clogged fuel filter can lead to several noticeable symptoms:
- Frequent Idling or Sputtering: If the vehicle starts fine but then shuts down when you try to stop, this could be due to insufficient fuel passing through the filter at low speed.
- Poor Acceleration: If the vehicle doesn’t respond appropriately when you try to accelerate, it could be due to a lack of fuel reaching the engine.
- Engine Misfires or Low Performance: A lack of fuel can cause the engine to misfire or perform poorly.
- Strong Odors: A clogged fuel filter can cause excess fuel to remain in the engine, leading to strong odors from the exhaust.
Troubleshooting a Clogged Fuel Filter
To confirm a clogged fuel filter, you can take the following steps:
- Replace the Fuel Filter: The simplest method is to replace the fuel filter. If the symptoms disappear, then the problem was likely a clogged fuel filter.
- Fuel Pressure Test: A mechanic can perform a fuel pressure test. Low fuel pressure could indicate a clogged filter.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Clogged Fuel Filter
Replacing a fuel filter is often within the capability of a DIY mechanic:
- Replacement: Obtain a replacement fuel filter (these are often inexpensive), and follow a guide or tutorial to replace it yourself. Always take care when working with fuel systems due to the risk of spillage or fire.
Costs of Fuel Filter Replacement
If you choose to have a professional replace the fuel filter, the cost can vary depending on your vehicle and local labor costs. On average, expect to pay between $50 and $150 for a fuel filter replacement, including parts and labor. Keep in mind, a severely clogged fuel filter can lead to more significant issues, like a damaged fuel pump, which would be more expensive to fix.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #4: Faulty Ignition Switch
The ignition switch is among the most significant electronic components that are common in many trucks and cars. It’s usually cited on the steering column behind the ignition lock cylinder. These two parts work together to power and start your car.
If your battery is in good condition but your car won’t turn on for a few tries, you may have a problem with your ignition switch. To narrow down the root of the problem, you can try turning on the headlights. Since the battery controls the dashboard and headlights, if they are turned on but the engine won’t start, the main problem could be a faulty ignition switch.
If you notice any of the following signs of a bad ignition switch, ensure to hire a professional to help get your car back in good condition. But what if there isn’t any noise from the starter? If you turn the key and don’t hear any noise, that’s a sign that something isn’t right. And this could be a result of a damaged electrical pathway. It can also be due to a dead battery.
How about if the car fails to start? If you turn the key and the vehicle fails to start, it could be due to a broken ignition switch.
Causes of a Faulty Ignition Switch
Well, what if you notice your key doesn’t turn? If you insert your key in the keyhole and it gets stuck and fails to turn to the ‘start’ position, you may likely have an issue with your vehicle’s ignition switch.
Yeah, but what if the dashboard lights start to flicker when the car is in motion? This is the least common sign of a faulty ignition switch, but it happens. If your dashboard lights flicker while your car is moving, this might indicate an issue with your car’s ignition switch.
The ignition switch plays a crucial role in starting your car. Here’s what can cause a faulty ignition switch:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the ignition switch can wear out from regular use. The contacts within the switch can corrode or become dirty, affecting its operation.
- Faulty Installation: If the ignition switch wasn’t installed correctly, it could cause problems. This could happen after replacing a faulty switch or during other repairs.
- Excessive Force: Using excessive force to turn the key can damage the ignition switch over time. This is particularly the case if you often carry a heavy keychain that puts additional strain on the switch.
Symptoms of a Faulty Ignition Switch
If the ignition switch isn’t working correctly, there can be several noticeable symptoms:
- No Noise from Starter: If you turn the key and there’s no noise, this could indicate a problem with the ignition switch.
- Failure to Start: If you turn the key and the car doesn’t start, this could be due to a broken ignition switch.
- Key Doesn’t Turn: If your key gets stuck and doesn’t turn to the ‘start’ position, this might indicate a faulty ignition switch.
- Dashboard Lights Flicker: If your dashboard lights flicker while driving, this could signal a problem with the ignition switch.
Troubleshooting a Faulty Ignition Switch
To confirm the ignition switch is the problem, you can:
- Test the Headlights: Try turning on the headlights. If they turn on, but the engine won’t start, this could point to an ignition switch problem.
- Check for a Dead Battery: If the battery is dead, the ignition switch won’t work. However, if the battery is good and the car still won’t start, it could be the ignition switch.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Faulty Ignition Switch
Repairing or replacing an ignition switch is typically a job for a professional mechanic due to the complexity of the work. However, if you’re experienced in car repairs, you can attempt it yourself.
Costs of Ignition Switch Replacement
Replacing an ignition switch can cost between $150 and $300, including parts and labor. The cost varies depending on your vehicle’s make and model and the labor costs in your area. If you don’t fix a faulty ignition switch, it could lead to more serious problems, like damage to the starter motor or alternator, which could incur additional costs.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #5: Gas Tank Is Empty
Running your car on an empty gas tank isn’t recommended because that means that there is no way to lubricate the gas pump, which utilizes fuel. Also, the engine may draw in air coupled with the last fuel residues into the gas pump. This air may prevent the engine from starting again since it throws the air-fuel mixture vital for combustion way off-kilter.
According to experts, it’s advisable to keep your gas tank at least a quarter full all the time. Apparently, doing this will help keep you out of dangerous situations when you’re low on gas and far from a gas station. However, there are other less apparent reasons to keep a slight amount of gas in your tank.
Now that you’re aware of the possible reasons why your vehicle won’t start with jump, let’s discuss how to troubleshoot the vehicle.
Causes of an Empty Gas Tank
Running out of fuel might seem like an obvious problem, but there are reasons why your gas tank might be empty:
- Forgetfulness: It’s easy to forget to check your fuel gauge, especially on short, familiar routes where you might not anticipate running out of fuel.
- Faulty Fuel Gauge: If your fuel gauge is faulty, it might not accurately reflect how much fuel is left in the tank.
- Unexpected Long Journey: If your journey was longer than expected, or you got stuck in traffic, you might have used more fuel than planned.
Symptoms of an Empty Gas Tank
The most obvious symptom of an empty gas tank is a car that won’t start. However, other symptoms could include:
- Engine Cuts Out: If you’re driving and your car suddenly cuts out, this could be due to an empty fuel tank.
- Fuel Warning Light: This light should illuminate on your dashboard when your fuel levels are low.
- Poor Acceleration: If your car struggles to accelerate, this could be due to low fuel levels.
Troubleshooting an Empty Gas Tank
To confirm that an empty gas tank is the problem, you can:
- Check the Fuel Gauge: If the gauge is showing empty or near-empty, this could be the issue. Bear in mind that the gauge might not be accurate if it’s faulty.
- Add Some Fuel: Add a small amount of fuel to the tank and attempt to start the car again.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for an Empty Gas Tank
Fixing an empty gas tank is straightforward: simply add more fuel. If you run out of fuel in an inconvenient location, you may need to call for roadside assistance or bring a jerry can of fuel to your vehicle.
Costs of Running Out of Fuel
While the cost of refueling your car will depend on current fuel prices, running out of fuel can lead to additional costs. For example, if you require roadside assistance, this can be expensive, especially if you’re not a member of a roadside assistance program.
Furthermore, frequently running your car on a nearly empty tank can lead to damage to the fuel pump, which can be costly to repair. As such, it’s always best to keep your fuel tank at least a quarter full to avoid these potential issues.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #6: Problem with the Starter Motor
Your car’s starter motor plays a crucial role in getting the engine running. If the starter motor is faulty or has failed, jump-starting your car won’t solve the problem. A clear symptom of a problematic starter is a clicking sound when you turn the key, but the engine doesn’t start.
You may also experience the starter running without engaging the engine. It’s always a good idea to get the starter motor checked by a professional if you’re experiencing these issues.
Causes of a Problematic Starter Motor
Here are the primary causes of a problematic starter motor:
- Age and Wear: Over time, the starter motor can wear out due to the normal aging process and constant use.
- Poor Maintenance: If the car isn’t regularly serviced, grime and dust can accumulate, causing the starter motor to fail.
- Electrical Problems: Loose connections or wiring issues can prevent the starter motor from functioning correctly.
Symptoms of a Faulty Starter Motor
Signs of a faulty starter motor can include:
- Clicking Sound: If you hear a clicking noise when you turn the key, but the engine doesn’t start, this could be a sign of a faulty starter.
- Starter Runs Without Engaging the Engine: If the starter motor is running but isn’t engaging with the engine, this could indicate a problem with the starter.
Troubleshooting a Faulty Starter Motor
To troubleshoot a problematic starter motor, consider the following steps:
- Check the Battery: Ensure that the battery is functioning correctly, as a dead battery can often be mistaken for a faulty starter.
- Look for Loose Connections: Check the connections to the starter motor to make sure they’re tight and secure.
- Test the Starter Motor: A mechanic can test the starter motor to confirm if it’s the problem or if something else is causing the issue.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Faulty Starter Motor
Fixing a starter motor typically involves replacing it, which is usually a job for a professional mechanic. If you’re experienced with car repairs, you could consider doing it yourself, but make sure to take all necessary safety precautions.
Costs of Starter Motor Replacement
The cost of replacing a starter motor can vary depending on the make and model of your car, ranging between $200 and $600 for both parts and labor. Ignoring a faulty starter can lead to further damage, resulting in additional repair costs. Therefore, it’s recommended to address any issues with your starter motor promptly.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #7: Failing Fuel Pump
The fuel pump delivers fuel from the tank to the engine. If it’s malfunctioning, it could be the reason your car isn’t starting despite a successful jump-start. A failed fuel pump can manifest in symptoms like a sputtering engine at high speeds, decreased fuel efficiency, and car stalling.
If you suspect a failing fuel pump, it’s best to have your vehicle checked by an auto expert to confirm and fix the issue.
Causes of a Failing Fuel Pump
Here are the main causes of a failing fuel pump:
- Wear and Tear: Like any other car component, fuel pumps are susceptible to wear and tear, especially if they’ve been in use for a long time.
- Dirty Fuel or Debris: If the fuel in your car is contaminated with dirt or debris, it can cause damage to the fuel pump over time.
- Running on a Low Gas Tank: Frequently driving your car with a near-empty gas tank can cause the fuel pump to overheat and wear out prematurely.
Symptoms of a Failing Fuel Pump
Common symptoms of a faulty fuel pump include:
- Engine Sputtering at High Speeds: If your engine begins to sputter or jerk while driving at high speeds, this could be a sign of a failing fuel pump.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: If you notice that your car is using more fuel than usual, a failing fuel pump could be the culprit.
- Car Stalling: If your car stalls, especially at high temperatures, this might be a sign that your fuel pump is on its way out.
Troubleshooting a Failing Fuel Pump
If you suspect your fuel pump is failing, consider the following:
- Check Fuel Pressure: A mechanic can test the pressure in your fuel line to see if the pump is delivering the correct amount of fuel.
- Listen for Noise: A high-pitched sound from your fuel tank, when the car is running, could indicate a problem with the fuel pump.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Failing Fuel Pump
Replacing a fuel pump usually requires a professional mechanic due to the complexity of the job and safety concerns around handling fuel. If you have the necessary skills and tools, you could attempt the repair yourself. Make sure to follow safety protocols when doing so.
Costs of Fuel Pump Replacement
The cost of replacing a fuel pump varies depending on your vehicle’s make and model, typically ranging from $300 to $600 including parts and labor. However, prices can go up for luxury or specialty vehicles. Ignoring a faulty fuel pump can lead to more serious engine damage, so it’s important to address this issue promptly.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #8: Broken Timing Belt
A broken or worn-out timing belt can also be a reason why your car won’t start even after a jump. This belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and the camshaft so that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times. If the timing belt breaks, the engine cannot run, and attempting to jump-start your car will be ineffective.
Causes of a Broken Timing Belt
Some potential causes of a broken timing belt include:
- Age and Wear: Timing belts deteriorate over time, and a high-mileage car is more likely to experience a broken timing belt.
- Incorrect Installation: If a timing belt is not installed correctly, it may fail prematurely.
- Severe Driving Conditions: If your vehicle frequently drives in high temperatures or carries heavy loads, it could stress the timing belt.
Symptoms of a Broken Timing Belt
Signs that your timing belt might be broken include:
- Engine Won’t Start: A broken timing belt will prevent the engine from turning over.
- Misfires or Rough Running: If the timing belt is worn but not yet broken, it may slip, causing the engine to misfire or run roughly.
- Oil Leak From Front of Motor: A worn timing belt can cause an oil leak at the front of the engine.
Troubleshooting a Broken Timing Belt
If you suspect a broken timing belt, these steps could confirm it:
- Visual Inspection: Remove the timing belt cover and visually inspect the belt for wear or damage.
- Crank the Engine: If the belt is broken, the engine will turn over quickly or have difficulty turning over.
DIY Fixes and Repairs for a Broken Timing Belt
Replacing a timing belt is a complex task typically best left to a professional mechanic. However, if you have experience with car repairs and the necessary tools, you could attempt the job. Always follow safety protocols when working on your vehicle.
Costs of Timing Belt Replacement
The cost of replacing a timing belt varies by vehicle make and model, but typically ranges from $300 to $700, including parts and labor. Ignoring a broken timing belt can cause severe engine damage, potentially requiring a full engine replacement, so it’s crucial to address a broken timing belt promptly.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #9: Blown Engine Fuse
Your car’s electrical system is safeguarded by various fuses, and if one connected to the engine management system blows, your car won’t start. This can often be overlooked as the issue, because many drivers aren’t aware of the fuses’ roles. Checking the fuses should be one of the first steps in your troubleshooting process if your car fails to start after a jump.
Causes of a Blown Engine Fuse
Engine fuses can blow due to:
- Electrical Overload: An electrical overload is the most common cause of a blown fuse. This could be from a faulty electrical device or a sudden power surge.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged or frayed wiring can lead to short circuits, which may blow a fuse.
- Age and Wear: Older fuses can become brittle and blow easily, even under normal electrical loads.
Symptoms of a Blown Engine Fuse
If an engine fuse is blown, you might notice:
- Engine Doesn’t Start or Run: The primary symptom of a blown engine fuse is that the engine doesn’t start or run.
- Loss of Functionality of Electrical Components: Depending on the fuse, you may lose the functionality of some electrical components like dashboard lights or the car radio.
Troubleshooting a Blown Engine Fuse
To check for a blown engine fuse:
- Inspect the Fuse Box: Refer to your vehicle’s manual to locate the fuse box. Carefully inspect the fuses, looking for any that appear burnt or broken.
- Test the Fuses: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the fuses. If a fuse has no continuity, it’s blown.
DIY Fixes for a Blown Engine Fuse
Replacing a blown engine fuse is a simple job you can do at home:
- Find the Correct Fuse: Refer to your vehicle’s manual to find the correct type and rating of the fuse.
- Remove and Replace the Fuse: Use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to remove the blown fuse and replace it with the new one.
Costs of Replacing an Engine Fuse
The cost of a replacement fuse is typically minimal, usually less than $5. However, a blown fuse is often a symptom of a larger electrical problem, which may need professional diagnosis and repair. This could potentially involve additional costs.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #10: Damaged Ignition Coil
The ignition coil transforms the battery’s low voltage to the thousands of volts needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs, igniting the fuel. If the ignition coil is damaged, this spark won’t occur, meaning the fuel cannot ignite and the engine won’t start.
Symptoms of a damaged ignition coil include backfiring, difficulty starting, or the vehicle stalling, even after a jump-start. If you suspect an issue with the ignition coil, it’s important to have it checked and replaced if necessary.
Causes of a Damaged Ignition Coil
Damage to an ignition coil can arise due to:
- Age and Wear: Over time, the ignition coil can wear out due to heat and vibration.
- Voltage Overload: If the ignition coil is supplied with too much voltage, it can get damaged.
- Bad Spark Plugs: Faulty or worn-out spark plugs can increase the voltage requirement, leading to coil failure.
Symptoms of a Damaged Ignition Coil
Indications of a damaged ignition coil include:
- Backfiring: This happens when unused fuel in the exhaust system ignites, causing loud noises from the exhaust.
- Difficulty Starting: If your car is hard to start, a failing ignition coil could be the reason.
- Vehicle Stalling: A damaged coil can lead to intermittent stalling as it fails to provide a consistent spark to the cylinders.
Troubleshooting a Damaged Ignition Coil
To diagnose a faulty ignition coil:
- Visual Inspection: Look for physical damage or oil leaks on the coil.
- Resistance Testing: Use a multimeter to test the primary and secondary resistance of the coil. Check with the manufacturer’s specifications.
DIY Fixes for a Damaged Ignition Coil
Replacing a damaged ignition coil can be a DIY job if you’re comfortable with auto repairs:
- Identify and Disconnect the Coil: Disconnect the battery, locate the ignition coil, and disconnect it from the system.
- Install the New Coil: Connect the new coil, reattach the battery, and test the car.
Costs of Replacing an Ignition Coil
The cost to replace an ignition coil can vary significantly, from around $70 to $300, including labor. If you choose to do it yourself, you’ll only have to pay for the part, which can range from $20 to $100.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #11: Inefficient Battery Terminals
The effectiveness of your jump-start attempt is largely dependent on the state of your battery terminals. If the terminals are loose or corroded, this could block the electrical flow from the donor battery, rendering your jump-starting efforts fruitless.
Corrosion appears as a white, powdery substance on the metal terminals. A simple cleanup might restore the connections, but sometimes replacing the battery is the best solution. Regularly inspect your battery terminals for signs of wear and corrosion to prevent this issue.
Causes of Inefficient Battery Terminals
Inefficient battery terminals can result from:
- Corrosion: This is usually a result of battery acid or hydrogen gas leakage from the battery, forming a white, powdery substance on the terminals.
- Loose Connections: Over time, battery terminals can loosen, resulting in poor electrical connectivity.
Symptoms of Inefficient Battery Terminals
Signs of inefficient battery terminals can include:
- Difficulty Starting the Car: Corroded or loose terminals can prevent the necessary electrical current from reaching the starter motor, causing difficulty in starting the car.
- Dim Lights: If the lights of the car are dim or flickering, this could indicate a problem with the battery terminals.
Troubleshooting Inefficient Battery Terminals
To diagnose inefficient battery terminals:
- Visual Inspection: Check for signs of corrosion or loose connections at the terminals.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to test if the correct voltage is being delivered from the battery.
DIY Fixes for Inefficient Battery Terminals
Fixing inefficient battery terminals can often be a DIY job:
- Clean the Terminals: Use a wire brush and a mixture of baking soda and water to clean away corrosion.
- Tighten the Connections: Ensure that the terminals are securely connected to the battery.
Costs of Repairing Inefficient Battery Terminals
If you choose to DIY, the cost of cleaning and tightening the terminals can be negligible. If the battery or terminals need to be replaced, costs can range from $50 to $200, depending on the battery’s brand and model. This cost includes both the price of the new battery and the labor involved in installing it.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #12: Unreliable Jumper Cables
The jumper cables you’re using could also be the culprit behind your unsuccessful jump-start. Jumper cables vary in quality, and if yours are low quality, too long, or too thin, they may not be able to carry the necessary current to start your car.
Damaged or worn-out cables can also fail in jump-starting a car. Always ensure your cables are in good condition and are rated for the correct current before using them.
Causes of Unreliable Jumper Cables
Unreliable jumper cables can be due to several reasons:
- Quality of the Cables: Not all jumper cables are created equal. Low-quality cables may not be capable of transmitting the required current to start a car.
- Cable Length and Thickness: Long or thin cables may cause a voltage drop due to resistance, resulting in insufficient current to start the car.
- Damaged or Worn Out Cables: Over time, jumper cables can wear out or get damaged, reducing their effectiveness.
Symptoms of Unreliable Jumper Cables
Unreliable jumper cables often show no physical symptoms. However, a consistent failure to jump-start a car despite a healthy battery in the donor vehicle can be a sign of unreliable cables.
Troubleshooting Unreliable Jumper Cables
- Visual Inspection: Check the cables for any visible damage or wear. Look for frayed wires, broken clamps, or corrosion.
- Test with Known-Good Cables: If you suspect that your cables might be the issue, try using another set of cables that are known to work.
DIY Fixes for Unreliable Jumper Cables
In most cases, the best solution for unreliable jumper cables is to replace them. When choosing new cables, consider the following:
- Choose the Right Gauge: The lower the gauge number, the thicker the wire, and the more current it can carry. A gauge of 4 to 6 is usually sufficient for most vehicles.
- Opt for Quality: Although they may be more expensive, high-quality cables are more reliable and last longer.
- Consider the Length: Shorter cables reduce the chance of a voltage drop but make sure they are long enough to reach from one battery to another.
Costs of Repairing Unreliable Jumper Cables
The cost to replace jumper cables can vary greatly depending on the brand, quality, and length of the cables. On average, you can expect to pay between $20 to $50 for a new set of reliable jumper cables.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #13: Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
The neutral or clutch safety switch is a feature designed to prevent your car from starting unless it’s in park or neutral for automatic transmissions, or the clutch pedal is pressed for manual transmissions. If this switch is damaged, the car won’t start, regardless of a successful jump-start.
If you’re facing issues even when your car is in the right gear, or you’re pressing the clutch pedal and still can’t start the car, the problem might be a damaged safety switch. It’s recommended to take your vehicle to a professional mechanic for proper diagnosis and repair.
Causes of a Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
The neutral or clutch safety switch may become compromised due to wear and tear over time, or due to physical damage to the switch or its wiring. This switch is designed to prevent the car from starting unless it’s in neutral or park for automatic transmissions, or unless the clutch pedal is fully depressed for manual transmissions.
Symptoms of a Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
Here are some signs that your neutral or clutch safety switch might be compromised:
- Car doesn’t start despite being in park or neutral: For automatic transmissions, if your car refuses to start while in park or neutral, the neutral safety switch could be the issue.
- Car doesn’t start despite the clutch pedal being depressed: For manual transmissions, if you have your clutch pedal fully depressed but the car still refuses to start, this could be a sign of a compromised clutch safety switch.
Troubleshooting a Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
If you suspect your neutral or clutch safety switch is compromised, it’s best to have your vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic. They have the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose and fix the issue.
DIY Fixes for a Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
It is possible to replace a faulty neutral or clutch safety switch yourself if you are mechanically inclined. However, the process can be complex and varies from one car model to another, so it’s usually best left to professionals.
Costs of Repairing a Compromised Neutral or Clutch Safety Switch
The cost to repair a compromised neutral or clutch safety switch varies based on your vehicle’s make and model and your location. However, on average, you can expect to pay between $100 to $200 for parts and labor. This includes the cost of the new switch and the labor to install it.
Car Won’t Start With Jump, Common Reasons #14: Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Engine Control Module (ECM) is the brain of your vehicle. It regulates a wide range of systems and functions, including ignition timing, fuel-air mixture, and more. If the ECU is damaged or malfunctioning, it can cause various issues, including preventing your car from starting.
In some cases, this might even occur after a successful jump-start. Having a professional diagnose any ECU issues is the safest and most efficient way to solve this problem.
Causes of a Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The Engine Control Unit (ECU), also known as the Engine Control Module (ECM), is a critical component of your vehicle. It regulates a variety of systems and functions, such as ignition timing and the fuel-air mixture. A damaged ECU can result from electrical issues, water damage, short circuits, or physical impact.
Symptoms of a Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
Here are some signs that your ECU might be damaged:
- Car doesn’t start or takes several attempts to start: The ECU plays a critical role in starting the car. A malfunctioning ECU can disrupt this process, making it difficult to start the vehicle.
- Engine performance issues: Since the ECU regulates the fuel-air mixture and ignition timing, any problems with the ECU could lead to a decrease in engine performance. This could include stalling, rough idling, or decreased fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine light is on: The ECU continuously monitors various systems of the vehicle. If it detects a problem, it will trigger the Check Engine light.
Troubleshooting a Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
If you suspect your ECU is damaged, it’s recommended to have your vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic. They have the tools and knowledge to accurately diagnose and fix ECU-related issues.
DIY Fixes for a Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
Repairing or replacing a damaged ECU should typically be left to professionals, as it involves intricate knowledge of the vehicle’s electronic systems. However, in some cases, a simple ECU reset or software update can resolve the issue.
Costs of Repairing a Damaged Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The cost to repair or replace a damaged ECU can be high due to the complexity of the unit. Depending on the make and model of your vehicle, it could range from $500 to $1500 or more, including parts and labor. However, the exact cost will vary based on the extent of the damage and the specific issue with the ECU.
How To Troubleshoot A Car That Won’t Start With Jump
Even after attempting a jump, the steps to troubleshoot your car’s inability to start are the same irrespective of your car’s model, make, or model year. While your car will often start without any issues while jump-starting, there are other instances where it will not (such as the ones mentioned above), prompting further investigation into the problem.
The following simple steps should be able to get your car started in no time and prevent it from being towed to a mechanic. However, in some instances, further repairs will be required to revert the vehicle to a good condition.
Car Won’t Start With Jump Fixes, Step 1
Let the dead battery stay in the vehicle for a few minutes while connected to jumper cables. If the battery is fragile, starting the vehicle immediately after connecting the cables may not provide the sufficient energy needed to start the car engine. In that case, you must allow the dead battery to charge up for a while to increase the chances of your vehicle starting.
Car Won’t Start With Jump Fixes, Step 2
Check if the protective rubber coating on the jumper cables is warm. If so, this implies an increase in resistance in the cables and minimal current flows to the battery. Try jump-starting the vehicle using a different set of cables.
Car Won’t Start With Jump Fixes, Step 3
Examine the output terminal on the battery. If you notice a green or chalky white substance on the battery, it means there’s corrosion which is curbing current flow. Detach the jumper cables and scrape off any corrosion. Connect the cables and try to start your vehicle again.
What Of Non-Battery-Related Issues
Step 1
Verify that there’s sufficient fuel in your car. Even if the gauge shows there’s fuel, it could have an electrical malfunction, and the fuel tank may be empty. Add approximately a gallon of fuel into the tank and attempt to restart the vehicle.
Step 2
Examine the fuel filter to see if it’s clogged and restricting the flow of fuel. Remove the fuel filter and see if it allows air through it. If air passes through, the fuel filter isn’t clogged. Therefore, consult your owner’s manual for removal instructions.
Step 3
Check the spark plugs to see if they are worn out, which prevents your vehicle from running smoothly, or on some occasions, does not allow it to start at all. Remove the spark plugs and examine the tips. If fuel is present or there’s a presence of black carbon build-up, it means they are worn and need replacement.
Extending Your Car Battery Life
As we mentioned earlier, one of the main problems behind your vehicle not starting is a dead or damaged battery. Typically, a car battery can last up to five years. These tips will help to extend your battery life and keep it in tip-top condition.
1. Limit Short Rides
Short rides to and from the block will cause an undercharge of your car battery. Uphold your battery’s life by frequently driving it and for more extended periods. However, if you hardly use your car that often, you can invest in a portable car battery jumper. A portable car charger can quickly jump-start your car battery without another car in case you are stranded.
2. Turn Off Your Car Lights When You Exit the Car
Accidentally leaving your car lights on can put a heavy toll on your car battery. To desist from forgetting more often, you can attach a note on your dashboard, park your car where you must pass through the headlights to reach your destination, or attach a tag on your car remote.
3. Ensure The Battery Is Tightly Fastened
A loose car battery could easily vibrate, resulting in short circuits or other internal damages. Have your battery terminal regularly checked by professionals – particularly if you often drive on bumpy roads – to ensure it’s appropriately and tightly mounted in the mounting bracket.
4. Avoid Using Electronics While Idling
Switch off functions like air conditioner, heat, or radio when your engine isn’t running to put less stress on your battery. Extending idling periods can also shorten your car’s battery life.
5. Control Corrosion
Although battery terminals often corrode over time, keeping them clean will help extend the life of your car battery. Clean the terminals using a toothbrush dipped in water and a baking soda mixture. Afterward, rinse the mixture off with cold water and followed with thorough drying using a clean cloth.
6. Conduct A Regular Battery Test
Paying attention to your battery’s condition matters if you’re looking to extend your car’s battery life. Carry out a regular battery test using a car battery tester to ascertain its output voltage level to know how well you preserve it and if you are due for a new battery.
7. Care For Your Entire Vehicle
Your vehicle consists of numerous parts working together. Ensure you’re taking care of your car by conducting routine tune-ups (to learn more, check out our guide on what is a tune-up and what does a tune-up consist of) and properly storing your car for an extended battery lifespan.
The battery, however, is just a single component of your car, so ensure you properly maintain every part of your car for an extended lifespan and to guarantee your car is operating at its best.
How To Fix A Car That Won’t Start
Fixing your car by yourself will entirely depend on the type of issue beforehand. If it’s a simple issue of replacing your battery, tightening the cables, or cleaning your battery terminal, you can do all these with basic mechanical skills and knowledge.
Make sure you’re aware of the precise cause of your vehicle not starting even after jump-starting so that the problem doesn’t recur and that you are not stranded. Besides, it will save you a lot of time and money on the road. It is always essential to hire a certified mechanic to examine and fix the problem.
Car Won’t Start
Besides the issue that we’ve looked into thus far, where your car won’t start with a jump, here are some other no-start scenarios that you might’ve experienced…
Car Won’t Start But Has Power
When your car won’t start but has power, it indicates that your battery isn’t the issue. The culprit could be a faulty starter motor. A malfunctioning ignition switch or fuel pump could also be to blame.
For diagnosis, turn on the headlights and try to start the car. If the lights dim significantly, it’s likely a weak battery. If they stay bright, consider getting a professional to check the starter motor and ignition switch.
Car Won’t Start Just Clicks
A car that won’t start and just clicks typically indicates a problem with the starter relay, starter motor, or a weak battery. Rapid clicking usually signals insufficient battery power. A single click can mean a faulty starter or relay. Inspecting these components can lead to the root cause. If the battery is fine, a mechanic should inspect the starter and relay.
Car Won’t Start in Cold
Cold weather can affect car batteries, thickening engine oil and making it harder for your car to start. If your car won’t start in the cold, it may be due to a weak battery, spark plug issues, or fuel line freeze-up. Regularly servicing your vehicle, using engine oil suitable for cold weather, and using an engine block heater can prevent these issues.
Car Won’t Start But Lights Come On
If your car won’t start but the lights come on, your battery may be sufficiently powering the lights but not your starter motor. Alternatively, it might be an issue with your ignition switch or a problematic anti-theft system. Check the dashboard for any warning lights and consult with a mechanic.
Car Won’t Start One Click Then Nothing
A car that won’t start with one click and then nothing could be experiencing issues with the starter motor, ignition switch, or battery. A faulty starter motor or a bad connection could be the cause. If the battery is not the issue, it’s time to inspect the starter motor and ignition switch.
Car Won’t Start No Noise
If your car won’t start and makes no noise, it could be due to a dead battery, a faulty ignition switch, or a problem with the fuel system. Without any noise, it’s tricky to diagnose the problem yourself. It’s best to get a professional mechanic involved to check these components.
Car Won’t Start But Radio Works
Just because your radio works doesn’t mean your battery is in perfect condition. Starting your car requires significantly more power than running the radio. A battery with insufficient charge may power the radio but not start the engine. If your car won’t start but the radio works, the battery, ignition switch, or starter could be the problem.
Car Won’t Start With Jump No Click
If a jump doesn’t start your car and you hear no click, it may be due to a faulty ignition switch, starter motor, or even a severe engine problem. Be sure to inspect the cables used for jumping as they could be the issue too. Professional help is advised to identify the root cause.
Car Won’t Start With New Battery
Sometimes, even a new battery can’t get your car to start. The problem could lie within the starter, ignition switch, or even a defective new battery. Alternator issues can also prevent your car from starting. Have a mechanic run a thorough check on these components.
Car Starts After Jump But Won’t Start Again
This indicates an issue with the charging system, usually the alternator. While jumping gives enough power to start, the alternator might not be supplying sufficient power to keep the car running. It’s best to get a mechanic to check your alternator if this is happening.
Car Won’t Start Battery Good
If your car won’t start even though the battery is good, it could be due to a bad starter motor, a faulty ignition switch, or a clogged fuel system. Check the sound your car makes when trying to start. If it clicks, it’s likely a starter motor or ignition switch issue. A mechanic should inspect these components.
Choosing The Right Mechanic
A good and reliable mechanic can help keep your car running for a more extended period and save you money on repairs. These hacks will help you find a reliable and professional mechanic to examine and fix your car.
1. Ask For Certifications
One of the fairly reliable certifications is the National Institute of Automotive Service Excellence (ASE). For a mechanic to acquire an ASE certification, they ought to go through extensive knowledge and skill testing as well as have a minimum of two years of relevant experience.
ASE, however, isn’t the only important certification. Other mechanics get certified by manufacturers to work on various car models. If a mechanic holds a manufacturer certification, this implies they have passed all the necessary tests and are thus experts in repairing various vehicles within their brand.
Keep in mind that individual mechanics are certified by manufacturers and ASE rather than auto shops. More often, you’ll be eager to know who’s working on your vehicle, and if possible, meet the mechanic.
2. Examine The Company’s Reputation
Today’s online platforms make it difficult for crooked businesses to get along for long. Various review websites offer insights into a company’s services to determine its reputation. One such website is Angi, a members-only site that offers auto service reviews from engine repair to car washes and body repair (fun fact, go check out our guide on how to buy a car wash).
It also has reviews on home maintenance-type services. Since companies can’t pay to be listed on Angi, and the website probes for phony reviews, you can be sure to get a candid opinion about the services offered by certain companies listed on that site.
3. Recommendations
Ask a family member, friend, or co-worker if they can recommend a suitable workshop or if there’s one they had a bad experience with. Check online for the workshop’s reviews. If you find that several people had a good experience with a similar shop, chances are you’ll also experience the same experience.
4. Visit The Workshop
If you happen to find a workshop that seems to be a good fit for car repair needs, visit them and ask some questions regarding their services. Will they show and explain to you what needs to be done?
Will they show you how the condition has been rectified or what has been replaced? How much do they charge for their services? If something wrong happens, what warranty do they offer? Do they have insurance cover for your car under their case or in case something goes south?
5. Look For Their Shop’s Affiliation
Does the shop exhibit a AAA Approved Auto Repair (AAR) Sign? The AAA screens shops for quality service. Auto-repair shops with AAR affiliation must sign an agreement to provide high-quality and reliable service performed solely by a certified mechanic. Besides, repair shops with AAR affiliation are guaranteed to be monitored for customer satisfaction and performance.
6. Trust Your Gut
If something about the mechanic puts you off, don’t leave them in your care, and later on blame yourself when something goes wrong. Trust your gut at all times; it can save you lots of grief. If you narrow it down to two or three mechanics who seem alike, the best move you can make is to go with the one that gives you the ultimate feeling.
The truth is that you can’t choose the best mechanic until you give them a try, but taking time to compare such things as qualifications, reputation, and price of the mechanic will offer you the best chance to find a reliable and professional mechanic.
Facts: Why Your Car Won’t Start After a Jumpstart
- Jumpstarting a car involves using another car’s battery and jumper cables to start your car.
- If your car won’t start after a jump, there are several possible reasons why.
- A completely dead or damaged battery, loose or corroded battery terminals, a bad alternator, a bad starter, or a bad neutral safety switch can all prevent your car from starting even with a jumpstart.
- Low-quality or improperly sized jumper cables can also prevent a successful jumpstart.
- Other issues beyond the starting system, such as a bad fuel pump (you can learn more in our guide on the signs of a fuel pump going bad), clogged fuel filter, or engine computer failure, can also prevent your car from starting after a jump.
- It is possible to fix some starting system issues, such as cleaning or tightening battery cables or replacing the battery, with basic mechanical skills.
- However, it is important to identify the exact cause of the problem to prevent it from happening again and save time and money in the long run.
- Consulting with a mechanic can help diagnose the issue and provide guidance on fixing it.
- Regular maintenance and checking the condition of your battery can help prevent starting issues.
- Keeping a set of quality jumper cables in your car and knowing how to use them can also help in case of a starting problem.
Car Won’t Start With Jump: In Conclusion…
With that said, as we’ve seen, there is a myriad of reasons why your car won’t start with jump. From a dead or faulty battery to a faulty ignition switch, empty gas, or clogged fuel filter, it can be an uphill task to determine the exact cause of the issue.
That’s why it is important to get your car to a repair shop and have a certified mechanic examine and eventually fix the problem.
FAQs On Car Won’t Start With Jump
If you’re still curious to learn more about why a car won’t start with a jump, our FAQs here might help…
How To Jump A Car
Jump-starting a car is pretty easy once you get the hang of it. First, find a working car, and have it parked whereby its battery is within easy reach of your car. Now, keep the ignition of both cars off, and with the parking brakes on (for safety). To jump a car, connect the red lead of the jumper cable to the positive terminal of both the dead and working battery on either car. Then, connect the black lead of the jumper cable to the negative terminal of the working battery. Meanwhile, attach its other black lead to an unpainted metal surface (away from the battery) as a grounding point. Finally, start the working car, and then start your car afterward to begin charging the battery.
Is Red Positive Or Negative
When you’re jump-starting a car, it’s crucial that you understand the red and black leads, and where they each go. The red lead on a set of jumper cables marks the positive (+) end, while the black lead marks the negative (-) end. When you’re connecting these leads to the battery terminals, make sure they match up. In other words, the red lead should be attached to the positive end (+ve) of the terminal, not the negative end (-ve). Ensure that you’ve identified the right lead and matching terminal, as incorrectly attaching them could lead to sparking or even an explosion.
How To Hook Up Jumper Cables
One of the most important aspects to consider when you’re jump-starting a car is hooking up the jumper cables properly. To put it simply, the red lead of the jumper cable must be connected to the positive end of both cars’ batteries (the working battery and the dead battery on the other car). Meanwhile, the black lead of the jumper cables needs to be connected in two ways. Firstly, on the car with the charged-up and working battery, the black lead has to be connected to the negative terminal. Meanwhile, on the car with the dead battery, the black lead needs to be attached to a metal ground – usually, an unpainted metal surface like the engine block, to complete the circuit.
Why Is My Car Not Starting
When your car isn’t starting up, there could be two key reasons why. Firstly, it’s possible that there’s an electrical fault in your car. For example, it may be a dead battery or a faulty alternator. Alternatively, a bad ignition switch and malfunctioning starter will also cause the car to not start. Or, it might also be attributed to worn-out spark plugs. Beyond that, a car’s failure to start might be caused by something more mechanical, instead. For instance, a clogged fuel filter, bad fuel pump, or dirty fuel injectors might make it so that no fuel is going to the engine. Thus, no combustion, and your car would fail to start.
Can You Jumpstart A Car With A Bad Alternator
Even if your alternator isn’t working right, it’s still possible to jump-start a car battery this way. However, with the faulty alternator not being able to produce a sufficient voltage that your car needs, it would need to run off the 12V battery entirely. Therefore, even if you could jump-start the battery and keep your car going, it wouldn’t go for too long, as the battery would eventually die due to a lack of charging from the malfunctioning alternator. On top of that, it’s never guaranteed that jump-starting with a bad alternator will work. For example, if the battery isn’t in good condition and can’t hold a sufficient charge, your car won’t start, regardless.
How to Use Jumper Cables
Using jumper cables is relatively straightforward, but should be handled with care. First, make sure both cars are off, and their keys are removed from the ignition. Place both cars close to each other, but they should not touch. Open both cars’ hoods. On each car’s battery, identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals. Attach one red clamp to the positive terminal of the dead battery, and the other end to the positive terminal of the good battery. Then, connect one black clamp to the negative terminal of the good battery, and the other end to an unpainted, metal part of the car with the dead battery. Start the working car for a few minutes, then try starting the dead car.
How to Jump Start a Car With Cables
To jump-start a car with cables, first, position another car with a working battery close to the dead car, but ensure they are not touching. Both cars should be turned off. Connect one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery and the other end to the positive terminal of the good battery. Connect one end of the black jumper cable to the negative terminal of the good battery and the other end to a grounded metal part of the dead car. Start the working car first, let it run for a few minutes, then attempt to start the car with the dead battery.
How to Start a Car With a Bad Starter
If your car has a bad starter, try the bump start method. This only works for cars with manual transmissions. Get the car moving with the help of gravity or by pushing. Once the car is rolling, press the clutch and shift into second gear. Let go of the clutch quickly. The momentum should turn the engine over, bypassing the starter. Remember, this isn’t a long-term solution, and your starter should be replaced as soon as possible.
Can You Jump a Car in the Rain
Yes, it’s possible to jump a car in the rain as long as you’re cautious. The main concern is safety, as water conducts electricity. Avoid standing in deep puddles while jump-starting and ensure your hands and the jumper cables are dry. Also, keep the car hoods open as little as possible to prevent the battery and cables from getting wet.
How Do I Know if My Alternator Is Bad
Signs of a bad alternator include dim or flickering headlights, a weak or dead battery, strange noises, electrical issues, or a warning light on your dashboard, typically shaped like a battery. Additionally, your car may have trouble starting or may stall because the alternator isn’t maintaining the battery’s charge. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advised to get your alternator checked.
When Your Car Won’t Start but All the Lights Come On
If your car won’t start but all the lights come on, it may be due to a variety of reasons. A faulty ignition switch, starter motor, or a discharged battery could be to blame. Another possibility is a problem with your car’s fuel system. Always listen for a clicking sound when you turn the key, as this could indicate a starter motor issue.
What Does the Battery Light Mean
The battery light on your dashboard generally indicates a charging system issue, which could be due to a malfunctioning alternator, problems with the serpentine belt, or a dying battery. This light illuminates when the battery isn’t being replenished properly or when the car is running solely on the battery power rather than from the alternator. When this light comes on, it’s advisable to get your car checked immediately to avoid being stranded with a dead battery.
How to Replace Alternator
To replace an alternator, first, disconnect the battery’s negative cable. Remove the serpentine belt or v-belt. Unplug the electrical connections from the alternator. Unbolt and remove the old alternator. Install the new alternator and tighten the bolts. Reconnect the electrical connections. Reinstall the belt, and finally, reconnect the battery. It’s a complex task, and if you’re not confident in your mechanical skills, it’s best left to a professional.
How Long Does It Take to Jump a Car
Typically, it can take anywhere from five to ten minutes to jump-start a car. This includes the time needed to set up the jumper cables and the time for the good battery to transfer some of its power to the dead battery. After connecting the cables, you should run the engine of the vehicle with a good battery for several minutes before attempting to start the car with a dead battery.
What Is the Alternator in a Car
An alternator is a critical component of a vehicle’s electrical system. It works with the battery to generate power for the electrical parts of the vehicle, like headlights and dashboard lights, and to charge the battery. The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which powers all electronic devices in the car and keeps the battery charged.
Why Won’t My Car Start but I Have Power
When your car won’t start but has power, the problem could be with the starter, ignition switch, or a faulty sensor. In some cases, a clogged fuel filter or issues with the fuel injectors could prevent the car from starting. Even though your vehicle’s electrical system is working, these issues can prevent the engine from cranking or firing.
How Long Does It Take to Replace an Alternator
The time it takes to replace an alternator varies depending on the make and model of the car, as well as your mechanical skill level. On average, it can take between two to three hours for a professional to replace an alternator. For someone less experienced, it may take longer. It’s a job that requires some knowledge and skill, as well as a range of tools.
Can You Jumpstart a Car With a Bad Alternator
You can jumpstart a car with a bad alternator, but it won’t keep running for long. The alternator’s job is to keep the battery charged, so once the jumpstart depletes, the car will lose power again. Therefore, while you might be able to start the car temporarily, you’ll need to replace the alternator for the vehicle to function correctly.
How to Start a Car With a Bad Fuel Pump
Starting a car with a bad fuel pump is tricky and not advisable. However, a temporary workaround can be attempting to start the car in ‘neutral’ or applying some external fuel pressure if your car allows it. Still, these are temporary fixes. A malfunctioning fuel pump requires immediate attention and should be replaced as soon as possible to avoid severe damage to the car’s engine.
How to Reconnect a Car Battery
To reconnect a car battery, first, ensure your car’s ignition is turned off. Start by connecting the positive (red) cable to the positive terminal of the battery. Make sure it’s secured tightly by tightening the nut using a wrench. Then, connect the negative (black) cable to the negative terminal and tighten it. Be sure not to touch the metal parts of the wrench to any other metal parts of the car while connecting the terminals, as it may cause sparks.
Why Won’t My Key Turn in My Car
If your key won’t turn in the ignition, it could be due to several reasons. The most common is a locked steering wheel. To unlock it, wiggle the steering wheel while turning the key. If that doesn’t work, your key may be worn or damaged, or there could be an issue with the ignition cylinder. Additionally, if the car isn’t in park or neutral, the key might not turn.
Why Is My Car Cranking but Not Starting
When your car is cranking but not starting, it means the starter is working, but the engine isn’t firing up. This could be due to a lack of fuel, insufficient spark, or lack of compression. Issues could range from a clogged fuel filter, faulty spark plugs, or sensor failures. It’s best to consult with a professional to diagnose the issue accurately.
When I Try to Start My Car It Just Clicks Rapidly
If you try to start your car and it just clicks rapidly, it’s likely due to a dead battery. Rapid clicking sounds often indicate that the battery doesn’t have enough power to crank the engine. The clicking sound is the starter trying to engage, but failing due to insufficient power. Other potential issues could include a bad starter or a faulty alternator.
How to Remove Jumper Cables
To remove jumper cables, follow the opposite order of how you connected them. First, remove the negative (black) clamp from the booster car, then the negative clamp from the dead car. Next, remove the positive (red) clamp from the booster car, then the positive clamp from the previously dead car. Always ensure the clamps don’t touch each other or any part of the car until they are safely stored away.
How to Start a Car With a Bad Ignition Switch
Starting a car with a bad ignition switch is not typically possible and isn’t recommended, as it can lead to dangerous situations or further damage. A faulty ignition switch needs to be replaced immediately. In urgent situations, some might attempt to hotwire the car, but this is illegal in many areas and can cause significant damage if not done correctly.
How to Jump a Car Without Jumper Cables
Jump-starting a car without jumper cables is usually done through a method known as push-starting. This method only works for cars with manual transmissions. To do it, you need to push the car until it gains some momentum, or have it roll down a hill, then quickly engage the clutch and put the car in second gear, then release the clutch to allow the engine to turn over and start.
How to Start a Car With a Dead Battery Without Another Car
If your car battery is dead and you don’t have another car to jump-start it, you can use a portable jump starter or battery charger. These devices can provide the necessary power to start your car. Simply connect the device to your car’s battery following the manufacturer’s instructions, and then attempt to start your car.
Why Is My Car Not Starting but the Battery Isn’t Dead
If your car isn’t starting but the battery isn’t dead, the problem could lie elsewhere. Issues could be with the ignition switch, the starter, the fuel system, or even the car’s security system. Also, check if the ‘Check Engine’ light is on. If it is, there could be a problem with the engine that needs to be checked out by a professional.
Why Is My Car Cranking but Not Starting
When your car is cranking but not starting, it usually indicates a problem with the fuel delivery, spark generation, or air intake system. The issue could be due to a variety of factors, including a bad ignition coil, a failed fuel pump, a blocked fuel filter, or problematic spark plugs. This issue should be diagnosed and fixed by a professional to ensure the correct resolution.
How Does a Steering Wheel Lock Work
A steering wheel lock is a safety feature that prevents the steering wheel from being turned, typically when the key is not in the ignition. This feature is designed to deter theft and unintentional movement of the car. When the steering wheel is turned after the key has been removed, a metal rod within the steering column drops into place, preventing further movement of the wheel.
How Long Does It Take to Change an Alternator
The length of time it takes to change an alternator can vary, depending on the model of the car and your level of mechanical expertise. On average, it can take a professional anywhere from two to three hours. For someone who isn’t as experienced, it may take longer. This is a complex task that requires specific tools and knowledge, so it’s often best left to a professional.
Why Won’t My Car Start in the Cold
Cold weather can affect your car’s ability to start for several reasons. Battery capacity is reduced in low temperatures, which can prevent the car from starting. The oil in your car can thicken when it’s cold, making it harder for the engine to turn over. Lastly, cold weather can lead to condensation in the fuel line, which can freeze and block the flow of fuel to the engine.
What Sensors Can Cause a Car Not to Start
Various sensors can cause a car not to start if they fail. These include the crankshaft position sensor, which measures the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft and sends this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). A failing camshaft position sensor can also cause starting issues, as it controls the engine’s timing. The Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor can also lead to starting problems, as it measures the amount of air entering the engine.
How to Take a Car Battery Out
To remove a car battery, start by turning off the car’s ignition. Disconnect the negative (black) battery cable first by loosening the connecting nut with a wrench, then do the same for the positive (red) cable. Next, you may have to remove a battery clamp or bracket. Once that’s done, lift the battery out carefully (it’s heavy), and ensure you don’t tip it as it contains acid.
Why Is My Car Making a Clicking Noise When I Try to Start It
If your car makes a clicking noise when you try to start it, it’s often a sign of a weak battery. This sound is the starter motor trying to turn over the engine, but it doesn’t have enough power from the battery. Other reasons might include a bad starter, faulty solenoid, poor wiring, or a bad alternator.
How Long to Run Car After Dead Battery
After jump-starting a dead battery, you should run the car for at least 15-30 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery. However, the exact time can vary depending on the age and condition of the battery. For an older battery, it may be better to drive the vehicle for an extended period or consider replacing the battery altogether.
What to Do If Car Battery Dies
If your car battery dies, you can attempt to jump-start it using another car and jumper cables or a portable jump starter. If the battery is old or has repeatedly died, it’s often better to replace it. Additionally, a continually dying battery might indicate a more significant problem, such as a failing alternator, which should be checked by a professional.
How to Fix Starter in Car
Fixing a starter in a car usually requires replacing it. Begin by disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery for safety. Then, locate the starter (typically near the rear of the engine or front of the transmission). Remove the mounting bolts and electrical connections, then remove the old starter. Install the new starter in the reverse order. This process can be complex, so it might be best to have a professional do it.
Why Don’t You Connect the Negative When Jumping a Car
When jumping a car, the final connection made with the jumper cables should be the negative cable to a grounded metal part of the dead car, not the negative terminal of the battery. This is because jump-starting a battery can cause a spark. If the battery is leaking, it can produce hydrogen gas, and a spark could ignite this gas causing an explosion.
How to Put Car in Neutral With Dead Battery
Most automatic cars can be shifted to neutral without power. You need to locate the brake shift interlock override slot (often found near the shifter). Then, insert a key or screwdriver into the slot, push down, and shift the car into neutral. For some models, the override slot might be hidden behind a cap or found on the steering column.
How Long Can You Drive With a Bad Starter
Driving with a bad starter can be unpredictable and risky as the starter could fail completely at any time, leaving you unable to start your car. If you suspect a starter issue, it’s recommended to have it inspected or replaced as soon as possible.
Will a Bad Starter Still Crank
In some cases, a bad starter can still crank the engine, but it may do so slowly, intermittently, or not effectively enough to start the car. You might hear a clicking sound, indicating that the starter solenoid is trying to engage, or the starter may run but not engage the flywheel to crank the engine.
What Causes a Starter to Go Bad
Starters can go bad for various reasons. Regular wear and tear are common, as the starter has a tough job in turning over the engine. A poor electrical connection, damaged components, or a malfunctioning solenoid can also lead to a bad starter. The heat from the engine can shorten the starter’s lifespan, and oil or fluid leaks can damage the starter too.
Why Won’t My Car Start in the Cold
Cold weather can affect your car’s starting ability. Cold temperatures reduce battery power, making it harder for the engine to turn over. The oil in your car can thicken when it’s cold, which can also make it harder to start. Furthermore, condensation can freeze in the fuel line, blocking fuel delivery to the engine.
Does Jump Starting a Car Damage the Computer
Jump-starting a car doesn’t typically damage the computer. However, if jump-starting is done incorrectly, such as reversing the polarity of the connections, it could cause a power surge that may damage the car’s electronic systems. It’s always important to connect the cables correctly and use a vehicle with a similar voltage to avoid such issues.
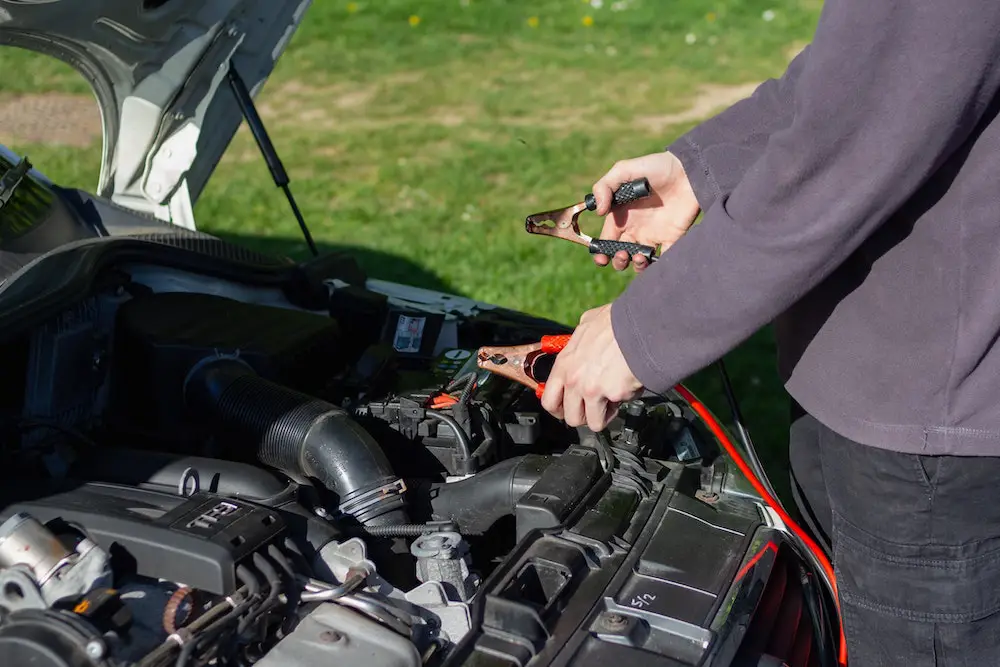


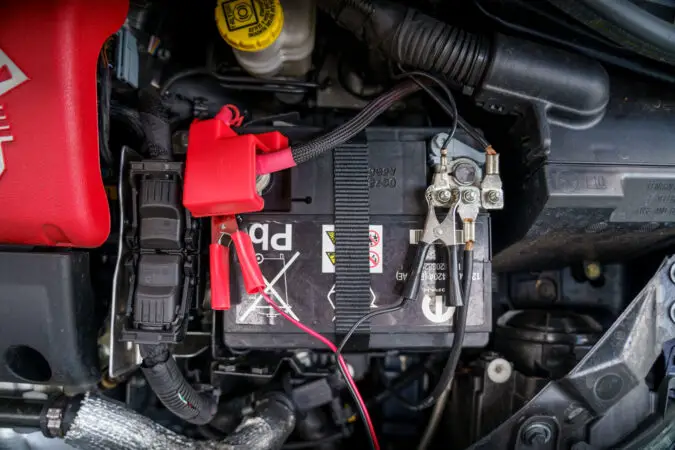



2 comments
Thanks for letting me know of the possible reasons a car won’t start. I find it interesting that even if your car battery is fine, an issue with your ignition switch could cause it to not run as intended. As I’ve never had to drive a car until now with my new job, I’m really worried that will happen to me. I’ll have to make sure to find a good vehicle battery jump start service in an area so that I won’t have to be stranded for long in case the company vehicle breaks down in the middle of the street.
Thanks for the comment, Tammie Houston!
Cheers, glad that our guide here has been of some help. If you’re regularly driving your car, especially longer distances, maybe you might consider getting one of those portable battery packs that also double as a go-anywhere jump-starter kit. They’re pretty handy to keep in your trunk as an emergency tool, just in case.